Many people have them in their houses LED bulbs, as they are much more economical and they don’t overheat like the traditional ones. But, have you ever wondered what are they made of? In this article, we will take a look at the different components that make up an LED bulb, and how they work together to create light.
What are the Components of LED Bulb?
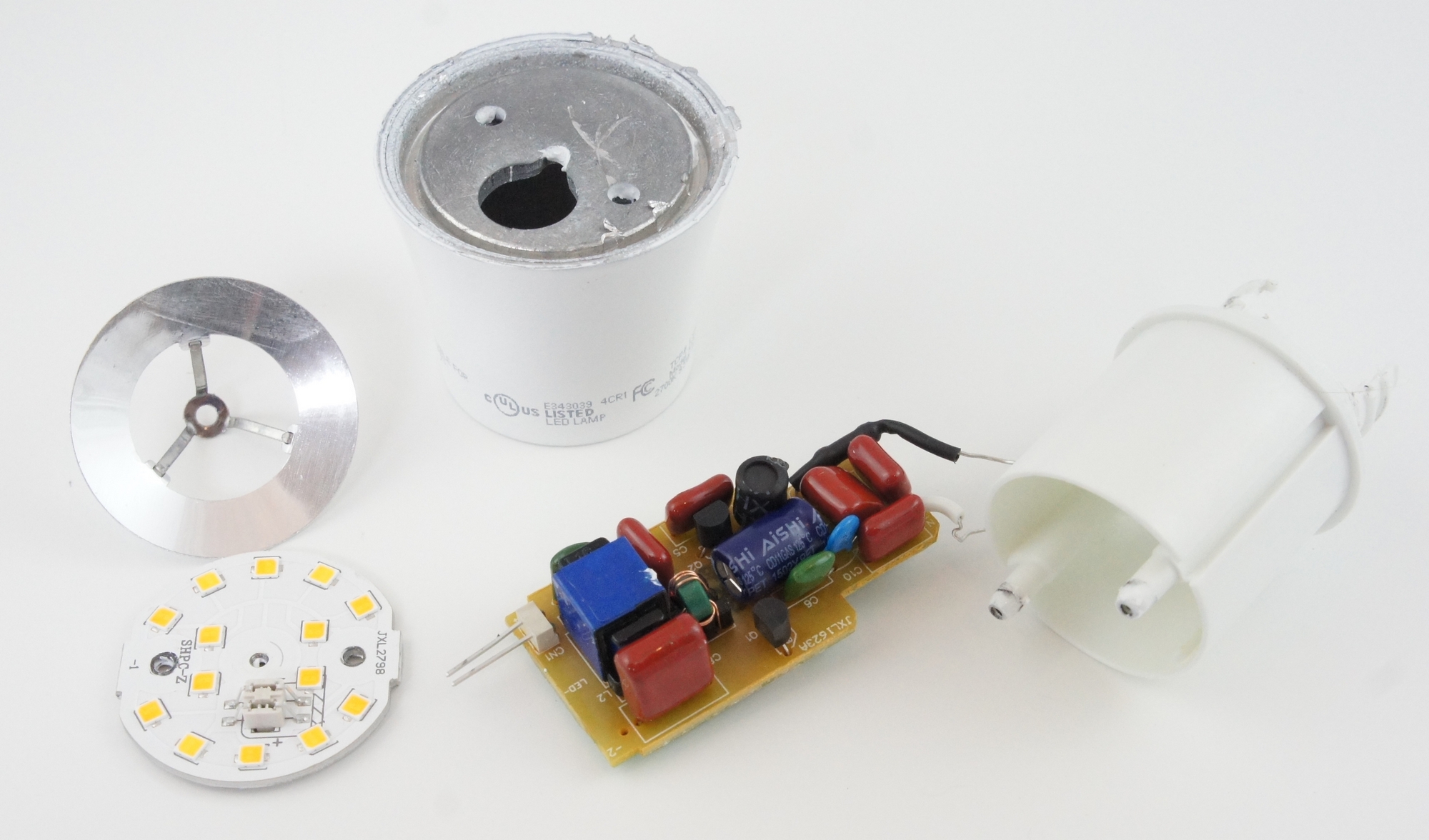

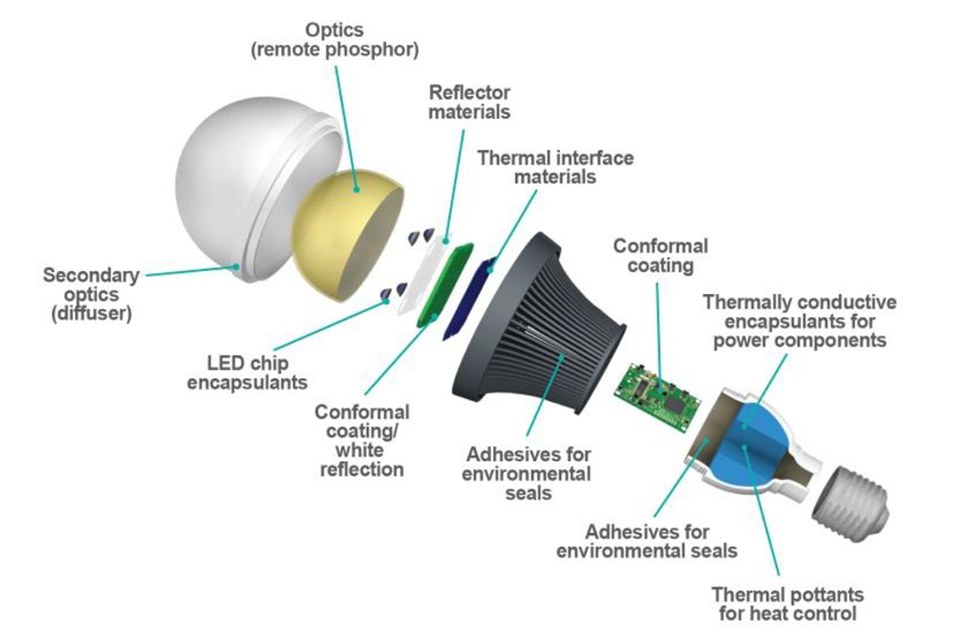
An LED light comprises an epoxy lens or casing, a wire bond, a reflecting chamber, a semiconductor wafer or diode, and a lead frame with two leads. The semiconductor wafer or diode that has been filled with faults is the fundamental component of an LED light.
The epoxy lens or casing protects the semiconductor wafer from damage. It also helps to focus the light that is emitted from the LED. The reflecting chamber is used to reflect any light that is not emitted directly from the LED back onto the semiconductor wafer. This helps to increase the efficiency of the LED. The lead frame has two leads that are used to connect the LED to a power source.
How do these components work together?
When an electric current is passed through the semiconductor wafer, it emits light. The epoxy lens or casing focuses this light and the reflecting chamber reflects any light that is not emitted directly from the LED back onto the semiconductor wafer. This increases the efficiency of the LED and makes it brighter. The lead frame is used to connect the LED to a power source. This provides the electric current that is needed to make the LED light up.
Each component plays its own role. For instance, an epoxy lens or casing is not just for focusing the light; it also protects the semiconductor wafer from any possible damage. A reflector chamber allows more light to be used and not wasted. A lead frame is essential in providing the electric current.
Now that we know the basics of what an LED bulb is made of, let’s take a more in-depth look at each individual component.
Epoxy lenses
They were invented in the early 60s and are made of bisphenol A polycarbonate. They have a high index of refraction, which makes them ideal for use in LED bulbs. Epoxy lenses help to focus the light that is emitted from the LED and they also protect the semiconductor wafer from damage.
Wire bonds
Wire bonds are made of gold or silver and they are used to connect the semiconductor wafer to the lead frame. Wire bonds help to conduct electricity and they also act as a heat sink, which helps to dissipate heat away from the semiconductor wafer.
Reflecting chambers
They were invented in the 1970s and they are made of dielectric materials such as silicon dioxide or quartz. Reflecting chambers help to reflect any light that is not emitted directly from the LED back onto the semiconductor wafer. This helps to increase the efficiency of the LED.
Semiconductor wafers
They are made of materials such as silicon, germanium, or gallium arsenide. Semiconductor wafers are used to create an electric current when an electric field is applied. This electric current is what causes the LED to emit light.
Lead frames
They are made of metals such as copper, aluminum, or brass. Lead frames have two leads that are used to connect the LED to a power source. The lead frame provides the electric current that is needed to make the LED light up.
Which Metal is Used in LED Bulb?
Arsenic, gallium, indium, and the rare-earth elements (REEs) cerium, europium, gadolinium, lanthanum, terbium, and yttrium are key mineral components utilized in LED semiconductor manufacturing. While other metals are used in smaller quantities for other purposes, these key components are utilized in large enough quantities that their supply availability can limit LED production.
A variety of mining and refining processes are used to produce the key rare-earth and metal minerals needed for LED semiconductor manufacturing. These processes start with the mining of mineral ores that contain the desired elements. The ores are then crushed and ground to a fine powder and undergo a series of physical and chemical processing steps to extract the desired elements. The extracted elements are then purified to meet the purity requirements for use in LED semiconductor manufacturing.
It`s interesting to know that the combination of gallium and arsenic is used to create a light-emitting diode, or LED. The first practical LED was created in 1962 by Robert Noyce, who also co-founded Intel Corporation. LEDs are now used in a wide variety of applications, including electronic devices, automotive lighting, and architectural lighting. While other metals are used in smaller quantities for other purposes, these key components are utilized in large enough quantities that their supply availability can limit LED production.
Which Gas is Used in LED Bulb?
LEDs are placed in a glass bulb that is the same as traditional incandescent bulbs. But helium gas is put in to help cool the LED. A typical LED has a lifespan of 50,000 hours. That’s longer than any other type of bulb. If we take another type of gas, let`s say, Krypton. It is also used in traditional light bulbs for the same reason - to help cool the filament. But in LED bulbs it is not needed, as there is no filament to heat up. Krypton is also used in halogen light bulbs.
Why neon gas is used in bulb?
The noble gases are neon, Argon, and Xenon. One of these elements' characteristics is that each atom has a full electron shell, so they don't react with one another and it takes a lot of energy to remove an electron. At either end of the tube is an electrode. When voltage is applied, the electrons "boil off" of the hot electrode and flow to the cool electrode, passing through the gas in between. The electrical resistance of the gas determines how much current will flow. Different gases produce different colors when excited in this way. Neon produces red, Argon produces blue, and Xenon produces white.
While other gases are used in smaller quantities for other purposes, these key components are utilized in large enough quantities that their supply availability can limit LED production.
Do LEDs contain silver?
Recently, several mineral processing engineers have developed a new method to extract valuable metals from light-emitting diode (LED) bulbs. These metals include silver, copper, gallium, and indium. The new method, which was developed by a team of researchers at the University of Kentucky, involves crushing LED bulbs and then separating the metals using a process called froth flotation.
Froth flotation is a process that uses chemicals to help separate desired materials from other materials in a mixture. After the metals have been separated, they can be further processed to extract individual metals. For example, silver can be extracted from copper-silver alloy using a process called electrolysis. This new method for recycling LED bulbs could help reduce the environmental impact of these products, as well as provide a new source of valuable metals.
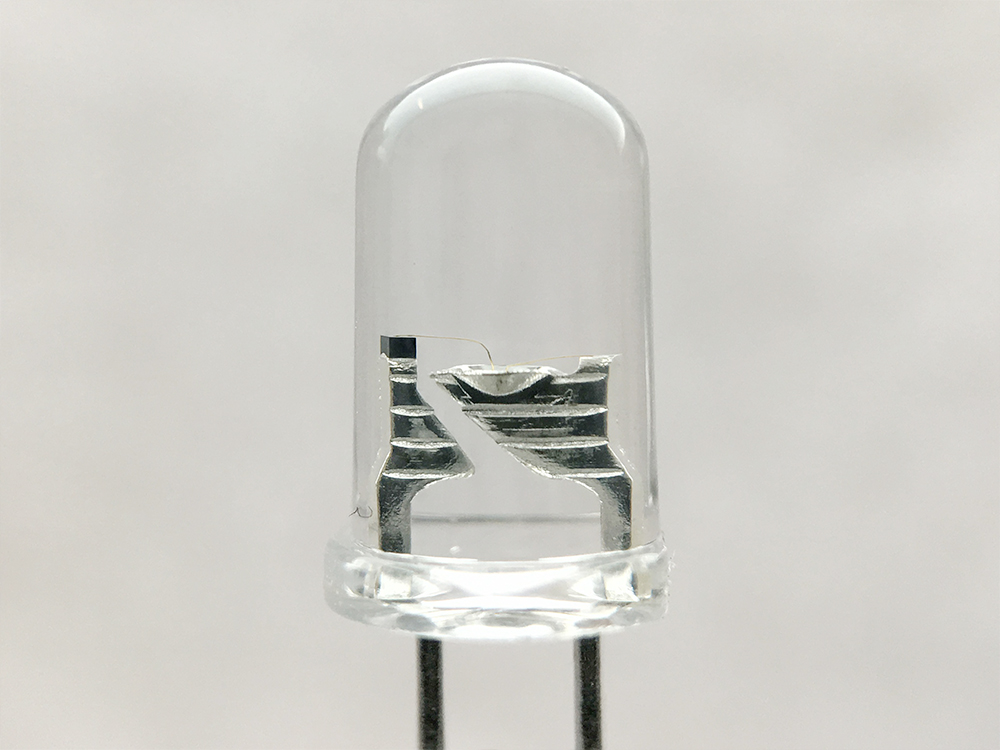

What about LED Strip Lights?
The constructions of little bulbs from the LED strips must vary from their bigger fellows. To make a classic light bulb, it is enough to add a glass case and filament to the semiconductor crystal. The further task of the manufacturers is to pump out all the oxygen from the case to increase the lifespan of the product. As for the LED strips, they do not need such a "little case". The thing is that you can not put more than 3-4 LEDs in one chip because of their cooling system. That is why they are used as long strings (up to 5 meters) placed on a special board called PCB.
LED strips consist of a series of connected diodes that emit light when electricity is passed through them. The strips are made up of several different types of LEDs, each of which emits a different color of light. The most common type of LED used in LED strips is the SMD5050 LED, which is a small chip that emits both red and green light.
Colors on the LED strips are created by mixing the light from the different LEDs. For example, a red LED and a green LED placed next to each other will create a yellow light. By mixing the light from different LEDs, it is possible to create any color of light.
What is the Difference between Ordinary and LED Bulbs Construction?
The main issue is that the light-emitting diodes don`t have a filament. The classic design of the bulbs foresees that the resistance of the conductor will make the electrons "boil" off it and turn into photons - particles of light. In the case of LEDs, they are made of materials that allow the electric current only in one direction. When you put the voltage on them, they start glowing.
The second significant contrast is that regular bulbs produce heat while functioning while LEDs release very little warmth even after running for hours. The reason behind it is that in classic incandescent lamps most of the energy (about 90%) transforms into heat while LED lights change no more than 20% of expended power into heat.
If we speak of halogen bulbs, they are almost the same as classic incandescent in construction. The only distinction is that they have a small amount of halogen gas that allows them to recycle the tungsten. Thanks to this, halogen incandescent light bulbs provide a more extended lifespan and brilliant light. To conclude, we may say that all three types of lamps have their pros and cons. The most significant advantage of LEDs is their extended lifespan and low heat emission. If you need bright light, then choose halogen incandescent bulbs or go for classics if you don`t mind changing them more often.
What Bulbs are Better: LEDs, Halogen, or Classic?

Nowadays the market offers a vast variety of light bulbs. Each type has its pros and cons. Let`s try to find out which one is better: LEDs, halogen, or classic? The most significant advantage of LEDs is their extended lifespan and low heat emission. If you need bright light, then choose halogen incandescent bulbs or go for classics if you don`t mind changing them more often.
Halogen bulbs are usually used when a lot of light is needed, for example, in car headlamps. The lifespan of a halogen bulb is about 2000 hours. They are less eco-friendly than LEDs and consume more energy. Classic incandescent bulbs have a short lifespan (about 1000 hours) but are the cheapest option. They are not as bright as halogen bulbs and consume more energy.
To conclude, we may say that all three types of lamps have their pros and cons. The most significant advantage of LEDs is their extended lifespan and low heat emission. If you need bright light, then choose halogen incandescent bulbs or go for classics if you don`t mind changing them more often.
Bottom Line
LED bulbs consist of a series of connected diodes that emit light when electricity is passed through them. The strips are made up of several different types of LEDs, each of which emits a different color of light. The most common type of LED used in LED strips is the SMD5050 LED, which is a small chip that emits both red and green light.
Colors on the LED strips are created by mixing the light from the different LEDs. For example, a red LED and a green LED placed next to each other will create a yellow light. By mixing the light from different LEDs, it is possible to create any color of light.